
Activity
AI4EC News
AI4EC News
Latest news
National Science Review: Knowledge Graphs + Large Language Models Empower Relay Catalysis Research
8/25/2025

 《Nature Communications》:界面效应主导的纳米限域水结构近日,汤富杰副教授课题组与德国马普学会高分子研究所Mischa Bonn教授、Yuki Nagata教授团队合作,在纳米尺度受限水结构研究领域取得重大突破。通过结合高精度理论光谱计算与和频振动光谱实验,研究团队首次证实:当水被限制在二维受限纳米空间时,其结构特性主要由界面化学性质决定,而非传统认为的几何限域效应;该规律在水层厚度大于8 Å(约3个水分子层)时始终成立,直至逼近分子级极限(<8 Å)才发生本质改变。这项创新性成果以《Interfaces Govern the Structure of Angstrom-Scale Confined Water Solutions》为题发表于国际知名期刊《Nature Communications》8/8/2025
《Nature Communications》:界面效应主导的纳米限域水结构近日,汤富杰副教授课题组与德国马普学会高分子研究所Mischa Bonn教授、Yuki Nagata教授团队合作,在纳米尺度受限水结构研究领域取得重大突破。通过结合高精度理论光谱计算与和频振动光谱实验,研究团队首次证实:当水被限制在二维受限纳米空间时,其结构特性主要由界面化学性质决定,而非传统认为的几何限域效应;该规律在水层厚度大于8 Å(约3个水分子层)时始终成立,直至逼近分子级极限(<8 Å)才发生本质改变。这项创新性成果以《Interfaces Govern the Structure of Angstrom-Scale Confined Water Solutions》为题发表于国际知名期刊《Nature Communications》8/8/2025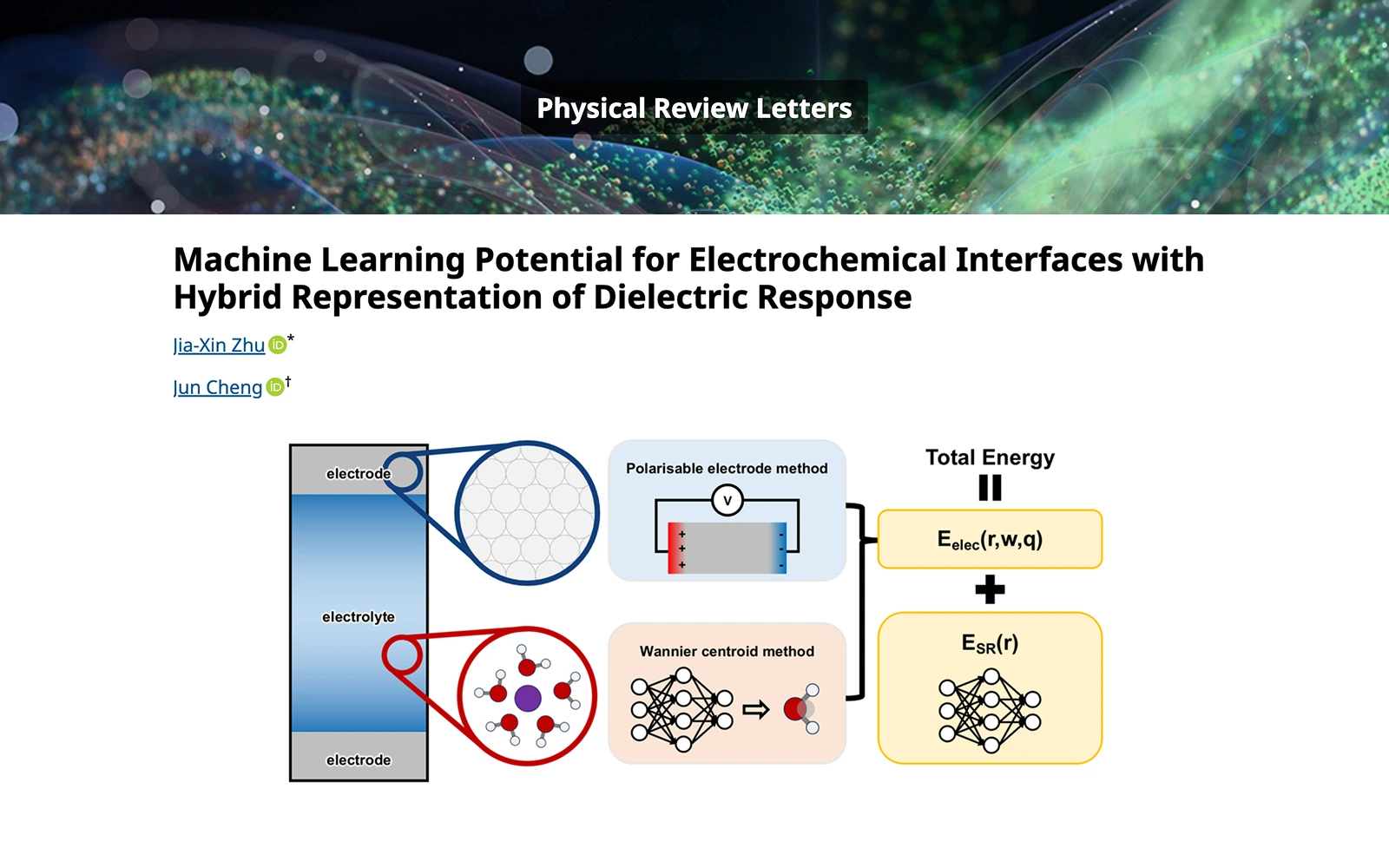 Physical Review Letters: Machine Learning Potential for Electrochemical Interfaces with Hybrid Representation of Dielectric ResponseRecently, the ec-MLP framework proposed by Xiamen University and the Laboratory of AI for Electrochemistry (AI4EC) of IKKEM has made significant progress in the method development of machine learning accelerated electrochemical interface simulations. The related research findings, titled "Machine Learning Potential for Electrochemical Interfaces with Hybrid Representation of Dielectric Response," were published in Physical Review Letters. In this work, the authors developed a hybrid framework to describe the dielectric response at the metal electrode-electrolyte interface, enabling the simultaneous descriptions of both the localized polarization of electrolyte and the non-local electronic responses of the metal electrode. This research provides a robust tool for the realistic and complex simulation of electrochemical interfaces. The first author of the study is Jia-Xin Zhu (2020 doctoral student in the College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering at Xiamen University). Professors Cheng Jun and Jia-Xin Zhu are serving as the corresponding authors.7/2/2025
Physical Review Letters: Machine Learning Potential for Electrochemical Interfaces with Hybrid Representation of Dielectric ResponseRecently, the ec-MLP framework proposed by Xiamen University and the Laboratory of AI for Electrochemistry (AI4EC) of IKKEM has made significant progress in the method development of machine learning accelerated electrochemical interface simulations. The related research findings, titled "Machine Learning Potential for Electrochemical Interfaces with Hybrid Representation of Dielectric Response," were published in Physical Review Letters. In this work, the authors developed a hybrid framework to describe the dielectric response at the metal electrode-electrolyte interface, enabling the simultaneous descriptions of both the localized polarization of electrolyte and the non-local electronic responses of the metal electrode. This research provides a robust tool for the realistic and complex simulation of electrochemical interfaces. The first author of the study is Jia-Xin Zhu (2020 doctoral student in the College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering at Xiamen University). Professors Cheng Jun and Jia-Xin Zhu are serving as the corresponding authors.7/2/2025 Focusing on AI-Empowered Electrochemistry Frontiers: Second International Symposium on AI for Electrochemistry (iSAIEC 2025) Successfully HeldFrom June 22-25, 2025, the Second International Symposium on AI for Electrochemistry (iSAIEC 2025) was successfully held at Xiamen University.6/26/2025
Focusing on AI-Empowered Electrochemistry Frontiers: Second International Symposium on AI for Electrochemistry (iSAIEC 2025) Successfully HeldFrom June 22-25, 2025, the Second International Symposium on AI for Electrochemistry (iSAIEC 2025) was successfully held at Xiamen University.6/26/2025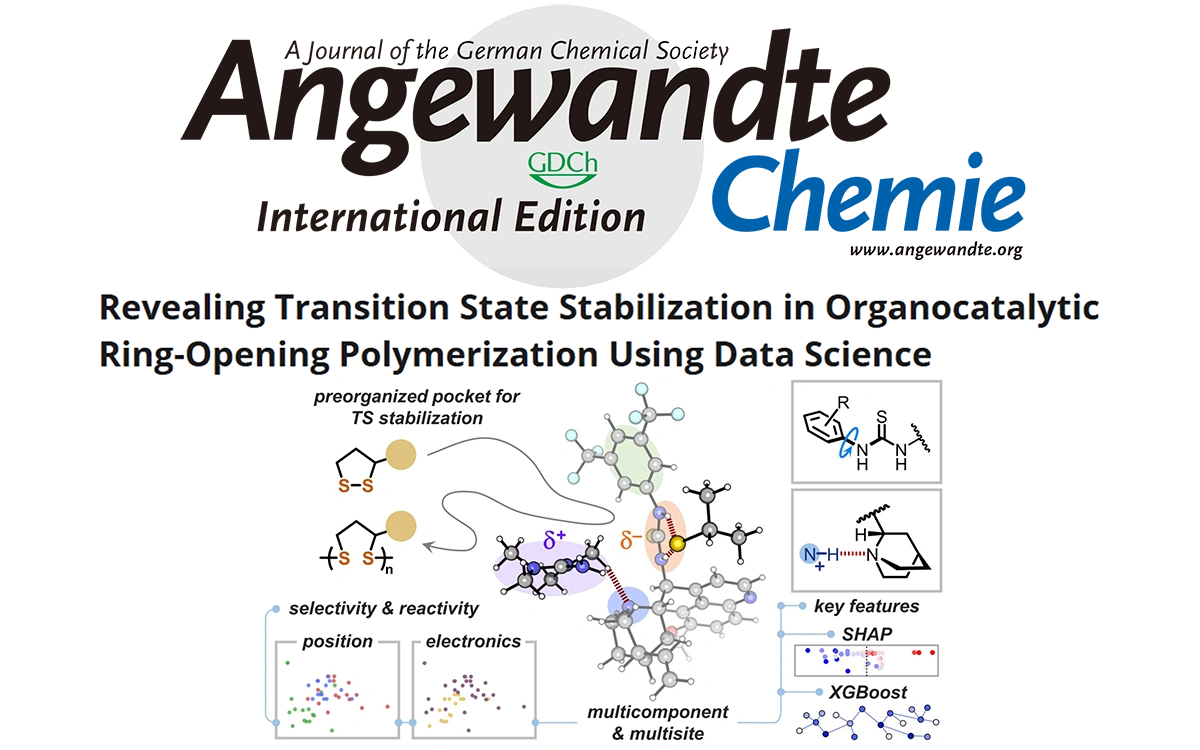 Angewandte Chemie International Edition: Revealing Transition State Stabilization in Organocatalytic Ring-Opening Polymerization Using Data Science近日,北京大学刘允研究员与厦门大学汪骋教授合作,开创性地采用数据驱动方法,揭示了硫脲催化1,2-二硫戊环开环聚合中过渡态的稳定机制,AI4EC Lab 助理研究员苏禹铭以共同一作的身份负责其中可解释机器学习部分的研究内容,包括描述符的设计以及特征降维的算法,最终启发化学家开发出了具有高活性和高区域选择性的催化剂分子。该研究成果发表于《德国应用化学》(Angewandte Chemie International Edition)。5/23/2025
Angewandte Chemie International Edition: Revealing Transition State Stabilization in Organocatalytic Ring-Opening Polymerization Using Data Science近日,北京大学刘允研究员与厦门大学汪骋教授合作,开创性地采用数据驱动方法,揭示了硫脲催化1,2-二硫戊环开环聚合中过渡态的稳定机制,AI4EC Lab 助理研究员苏禹铭以共同一作的身份负责其中可解释机器学习部分的研究内容,包括描述符的设计以及特征降维的算法,最终启发化学家开发出了具有高活性和高区域选择性的催化剂分子。该研究成果发表于《德国应用化学》(Angewandte Chemie International Edition)。5/23/2025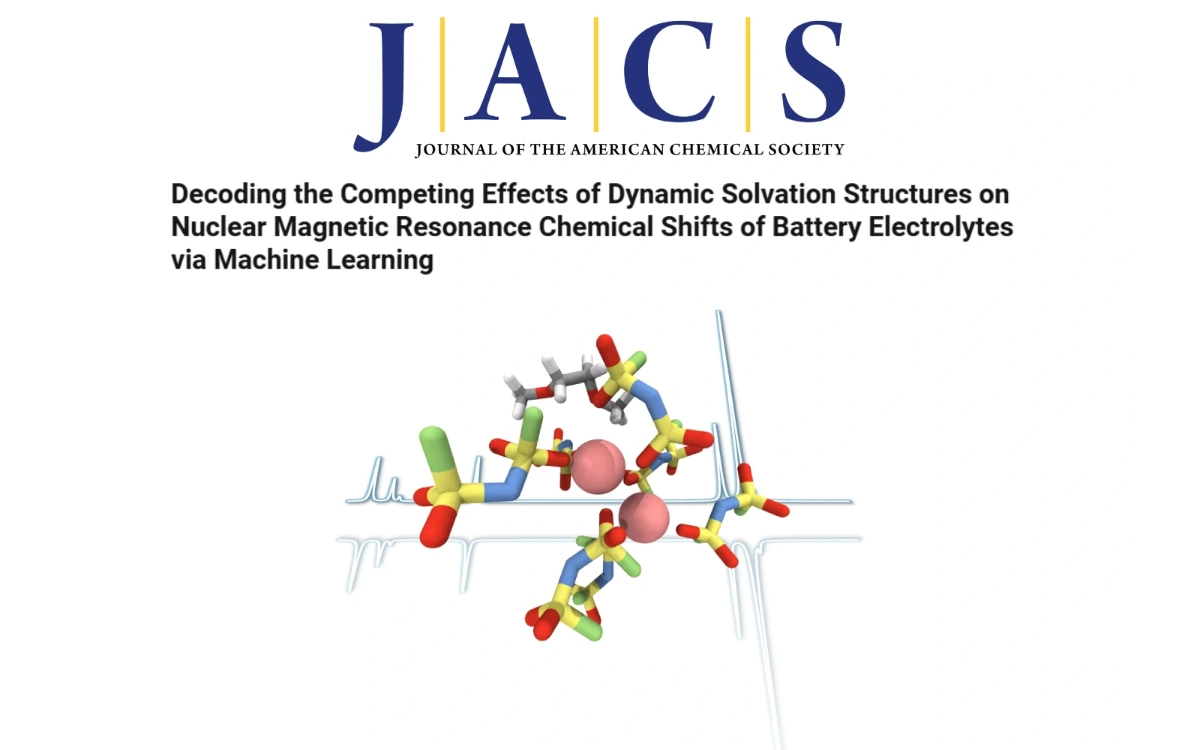 《Journal of the American Chemical Society》:机器学习核磁共振谱揭示电解质动态溶剂化结构的竞争效应近日,厦门大学与嘉庚创新实验室AI4EC Lab利用机器学习联用方法,在计算电解液动态核磁共振(NMR)谱解析领域取得重要突破,实现了对双氟磺酰亚胺锂(LiFSI)/二甲醚(DME)电解液中动态的⁷Li核磁共振化学位移的预测。预测结果精准揭示了⁷Li核磁共振化学位移的反转现象,与实验观测结果吻合。该成果是团队继电池正极材料动态核磁谱研究和NMRNet深度学习框架之后,在相关领域的又一次方法迭代与体系应用拓展,相关研究成果已发表于顶级化学期刊《Journal of the American Chemical Society》。4/19/2025
《Journal of the American Chemical Society》:机器学习核磁共振谱揭示电解质动态溶剂化结构的竞争效应近日,厦门大学与嘉庚创新实验室AI4EC Lab利用机器学习联用方法,在计算电解液动态核磁共振(NMR)谱解析领域取得重要突破,实现了对双氟磺酰亚胺锂(LiFSI)/二甲醚(DME)电解液中动态的⁷Li核磁共振化学位移的预测。预测结果精准揭示了⁷Li核磁共振化学位移的反转现象,与实验观测结果吻合。该成果是团队继电池正极材料动态核磁谱研究和NMRNet深度学习框架之后,在相关领域的又一次方法迭代与体系应用拓展,相关研究成果已发表于顶级化学期刊《Journal of the American Chemical Society》。4/19/2025 Nature Computational Science: Toward a unified benchmark and framework for deep learning-based prediction of nuclear magnetic resonance chemical shiftsRecently, a joint team from the College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Pen-Tung Sah Institute of Micro-Nano Science and Technology, Institute of Artificial Intelligence, AI4EC Lab of the Tan Kah Kee Innovation Laboratory, Beijing AI for Science Institute, and DP Technology has achieved a significant advance in nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectral analysis with the deep-learning framework NMRNet. Published in Nature Computational Science under the title “Toward a unified benchmark and framework for deep learning-based prediction of nuclear magnetic resonance chemical shifts,” the work introduces an innovative SE(3) Transformer architecture that delivers high-accuracy chemical-shift predictions for both solution-state and solid-state NMR, providing a powerful new tool for molecular structure elucidation and materials design.该项研究成果的第一作者为厦门大学化学化工学院硕士生徐凡杰,第二作者为加州大学戴维斯分校郭文韬博士(现为加州理工学院博士后),通讯作者为厦门大学程俊教授和汤富杰副教授、深势科技算法研究员高志锋。合作者包括嘉庚创新实验室副研究员王锋,以及深势科技算法研究员么琳和汪鸿帅。该研究受到田中群院士和鄂维南院士的指导,并得到北京科学智能研究院院长张林峰的支持。3/28/2025
Nature Computational Science: Toward a unified benchmark and framework for deep learning-based prediction of nuclear magnetic resonance chemical shiftsRecently, a joint team from the College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Pen-Tung Sah Institute of Micro-Nano Science and Technology, Institute of Artificial Intelligence, AI4EC Lab of the Tan Kah Kee Innovation Laboratory, Beijing AI for Science Institute, and DP Technology has achieved a significant advance in nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectral analysis with the deep-learning framework NMRNet. Published in Nature Computational Science under the title “Toward a unified benchmark and framework for deep learning-based prediction of nuclear magnetic resonance chemical shifts,” the work introduces an innovative SE(3) Transformer architecture that delivers high-accuracy chemical-shift predictions for both solution-state and solid-state NMR, providing a powerful new tool for molecular structure elucidation and materials design.该项研究成果的第一作者为厦门大学化学化工学院硕士生徐凡杰,第二作者为加州大学戴维斯分校郭文韬博士(现为加州理工学院博士后),通讯作者为厦门大学程俊教授和汤富杰副教授、深势科技算法研究员高志锋。合作者包括嘉庚创新实验室副研究员王锋,以及深势科技算法研究员么琳和汪鸿帅。该研究受到田中群院士和鄂维南院士的指导,并得到北京科学智能研究院院长张林峰的支持。3/28/2025 Conference Notice | AI-Accelerated Dynamic Catalysis Free Energy Calculation WorkshopThe AI-Accelerated Dynamic Catalysis Free Energy Calculation Workshop will be held on April 12, 2025, at Xiamen University Siming Campus! This workshop invites experts in the field to teach research progress in dynamic catalytic theoretical calculations, covering topics from catalytic reaction mechanism research, machine learning acceleration methods, to workflow software usage. By closely integrating advanced machine learning methods and automated tools with catalytic theoretical research, it will demonstrate their capabilities in solving complex dynamic catalytic problems.3/21/2025
Conference Notice | AI-Accelerated Dynamic Catalysis Free Energy Calculation WorkshopThe AI-Accelerated Dynamic Catalysis Free Energy Calculation Workshop will be held on April 12, 2025, at Xiamen University Siming Campus! This workshop invites experts in the field to teach research progress in dynamic catalytic theoretical calculations, covering topics from catalytic reaction mechanism research, machine learning acceleration methods, to workflow software usage. By closely integrating advanced machine learning methods and automated tools with catalytic theoretical research, it will demonstrate their capabilities in solving complex dynamic catalytic problems.3/21/2025 AI4EC Lab's Latest Achievement Selected as APS Highlight PaperOn March 11, 2025, the American Physical Society (APS) selected the groundbreaking research published by Associate Professor Tang Fujie (iKKEMLab AI4EC Lab, Xiamen University) in the top-tier physics journal "Physical Review X" - "Many-body Quantum Theory Study on the Ordering of Quasi-One-Dimensional Water Molecular Chains in Hydrogen-Bond Networks Probed by Visible Light Absorption Spectroscopy" - as a highlight paper. Professors Davide Donadio from UC Davis and Giulia Galli, a member of the US National Academy of Sciences from the University of Chicago, specifically wrote a news commentary titled "Shedding Light on Water Wires" in the APS magazine "Physics" for this groundbreaking research.3/11/2025
AI4EC Lab's Latest Achievement Selected as APS Highlight PaperOn March 11, 2025, the American Physical Society (APS) selected the groundbreaking research published by Associate Professor Tang Fujie (iKKEMLab AI4EC Lab, Xiamen University) in the top-tier physics journal "Physical Review X" - "Many-body Quantum Theory Study on the Ordering of Quasi-One-Dimensional Water Molecular Chains in Hydrogen-Bond Networks Probed by Visible Light Absorption Spectroscopy" - as a highlight paper. Professors Davide Donadio from UC Davis and Giulia Galli, a member of the US National Academy of Sciences from the University of Chicago, specifically wrote a news commentary titled "Shedding Light on Water Wires" in the APS magazine "Physics" for this groundbreaking research.3/11/2025 《Physical Review X》:可见光吸收光谱揭示氢键网络中准一维水分子链有序性的多体量子理论研究科学家首次通过可见光吸收谱“看见”了自然界中神秘的“水线”(water wires)!日前,来自美国天普大学、厦门大学/嘉庚创新实验室人工智能应用电化学实验室和耶鲁大学的研究团队在国际顶级物理学期刊《Physical Review X》上发表突破性研究,论文链接为:https://journals.aps.org/prx/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevX.15.011048。该项突破性研究还被美国物理学会(APS)选为亮点论文。3/6/2025
《Physical Review X》:可见光吸收光谱揭示氢键网络中准一维水分子链有序性的多体量子理论研究科学家首次通过可见光吸收谱“看见”了自然界中神秘的“水线”(water wires)!日前,来自美国天普大学、厦门大学/嘉庚创新实验室人工智能应用电化学实验室和耶鲁大学的研究团队在国际顶级物理学期刊《Physical Review X》上发表突破性研究,论文链接为:https://journals.aps.org/prx/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevX.15.011048。该项突破性研究还被美国物理学会(APS)选为亮点论文。3/6/2025 《Nature Nanotechnology》:AI–nano-driven surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for marketable technologiesThe 50th anniversary of its discovery underscores surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) as one of the oldest and most dynamic branches of nanoscience and nanotechnology. The time has come for nanostructure-based SERS to integrate artificial intelligence (AI) tools and overcome current commercialization challenges.1/25/2025
《Nature Nanotechnology》:AI–nano-driven surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for marketable technologiesThe 50th anniversary of its discovery underscores surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) as one of the oldest and most dynamic branches of nanoscience and nanotechnology. The time has come for nanostructure-based SERS to integrate artificial intelligence (AI) tools and overcome current commercialization challenges.1/25/2025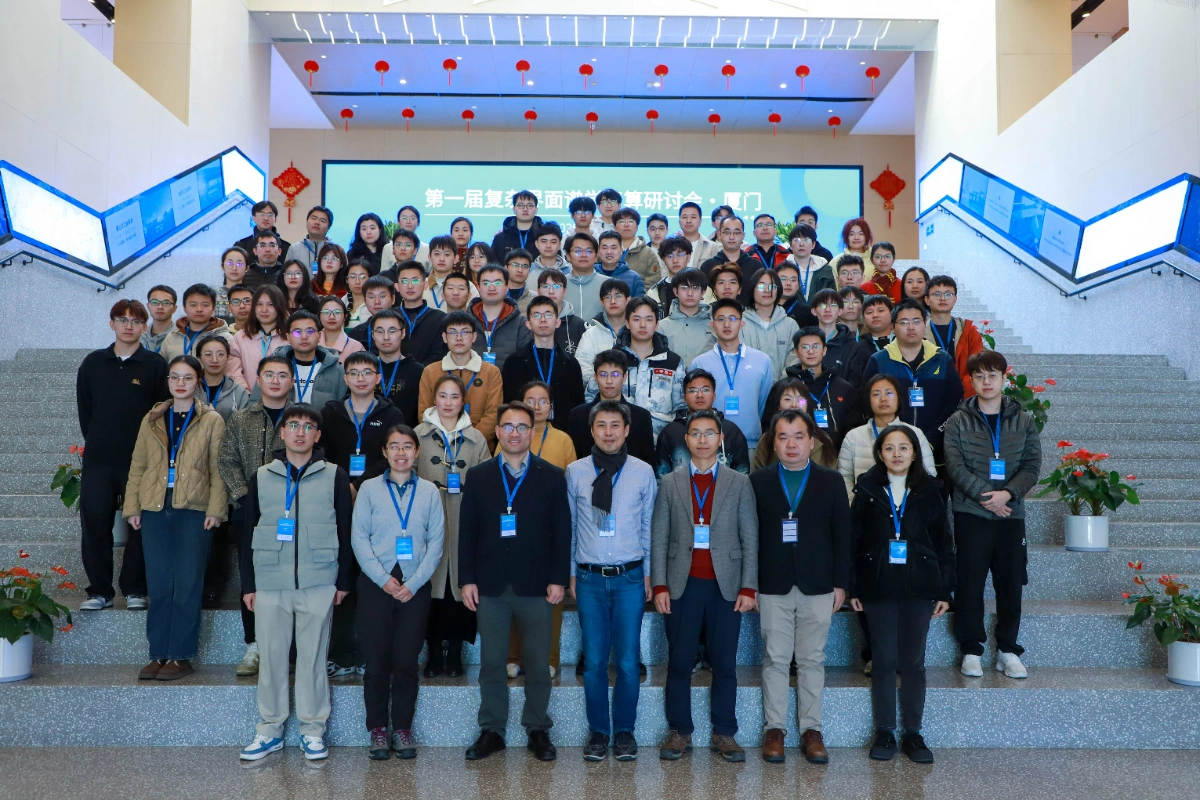 The First Workshop on Intelligent Computing for Spectroscopy at Complex Interfaces Successfully Held at Xiamen University2025年1月13日-15日,第一届复杂界面智算谱学研讨会成功举办。会议收到了来自全国各地50所高校和科研机构的200余名师生报名,线下招收学员80人,线上全程共吸引80,000余人在线观看。部分报告内容近期将上传AI4EC官网与玻尔科研空间站. AI4EC Lab也将持续推动AI辅助计算谱学的理论与算法发展,与领域内研究人员共同探索复杂界面的谱构效关系解析!1/21/2025
The First Workshop on Intelligent Computing for Spectroscopy at Complex Interfaces Successfully Held at Xiamen University2025年1月13日-15日,第一届复杂界面智算谱学研讨会成功举办。会议收到了来自全国各地50所高校和科研机构的200余名师生报名,线下招收学员80人,线上全程共吸引80,000余人在线观看。部分报告内容近期将上传AI4EC官网与玻尔科研空间站. AI4EC Lab也将持续推动AI辅助计算谱学的理论与算法发展,与领域内研究人员共同探索复杂界面的谱构效关系解析!1/21/2025 Conference Notice | First Complex Interface Spectroscopy Intelligent Computing Workshop NoticeThe First Complex Interface Spectroscopy Intelligent Computing Workshop will be held on January 13-15, 2025, at the Xiang'an campus of Xiamen University. We have invited domestic and international experts to teach computational simulation methods for common spectroscopy, covering vibrational spectroscopy of complex interfaces (infrared, Raman, sum frequency spectroscopy), solid-state NMR spectroscopy, X-ray spectroscopy (including X-ray absorption spectroscopy, X-ray scattering spectroscopy, etc.), atomic force microscopy, and data-driven spectroscopic processing methods.11/5/2024
Conference Notice | First Complex Interface Spectroscopy Intelligent Computing Workshop NoticeThe First Complex Interface Spectroscopy Intelligent Computing Workshop will be held on January 13-15, 2025, at the Xiang'an campus of Xiamen University. We have invited domestic and international experts to teach computational simulation methods for common spectroscopy, covering vibrational spectroscopy of complex interfaces (infrared, Raman, sum frequency spectroscopy), solid-state NMR spectroscopy, X-ray spectroscopy (including X-ray absorption spectroscopy, X-ray scattering spectroscopy, etc.), atomic force microscopy, and data-driven spectroscopic processing methods.11/5/2024 《The Journal of Chemical Physics》:通过基于机器学习的计算振动光谱揭示α-Al₂O₃(0001)-水界面的微观结构2024年9月24日,国际知名物理化学期刊J. Chem. Phys.在线发表了厦门大学汤富杰副教授和程俊教授课题组的研究论文,题目为《Revealing the molecular structures of α-Al₂O₃(0001)–water interface by machine learning based computational vibrational spectroscopy》,论文的第一作者为Xianglong Du。该论文被编辑评为“Editor's Pick”,编辑每年在两千多篇论文中精选四十余篇,旨在选出物理化学领域最有创新性和影响性的论文。此外该论文是应客座编辑邀请参与的纪念著名非线性光学大家沈元壤教授专刊“Festschrift in honor of Yuen-Ron Shen”,该专刊用来介绍非线性光学的发展以及在表/界面相关问题研究领域中的顶尖科学家的贡献。9/30/2024
《The Journal of Chemical Physics》:通过基于机器学习的计算振动光谱揭示α-Al₂O₃(0001)-水界面的微观结构2024年9月24日,国际知名物理化学期刊J. Chem. Phys.在线发表了厦门大学汤富杰副教授和程俊教授课题组的研究论文,题目为《Revealing the molecular structures of α-Al₂O₃(0001)–water interface by machine learning based computational vibrational spectroscopy》,论文的第一作者为Xianglong Du。该论文被编辑评为“Editor's Pick”,编辑每年在两千多篇论文中精选四十余篇,旨在选出物理化学领域最有创新性和影响性的论文。此外该论文是应客座编辑邀请参与的纪念著名非线性光学大家沈元壤教授专刊“Festschrift in honor of Yuen-Ron Shen”,该专刊用来介绍非线性光学的发展以及在表/界面相关问题研究领域中的顶尖科学家的贡献。9/30/2024 "Global Alliance for Scientific Intelligence Development" Initiative Launched in BeijingIn response to the trends of the artificial intelligence era and national strategic needs, and to promote the application and development of artificial intelligence technology in the field of scientific research, on August 23, scholars and experts from 30 institutions including Peking University, Beijing Institute of Scientific Intelligence, and iKKEMLab convened at Zhongguan Xin Yuan, Peking University, to initiate the establishment of the "Global Alliance for Scientific Intelligence Development".8/29/2024
"Global Alliance for Scientific Intelligence Development" Initiative Launched in BeijingIn response to the trends of the artificial intelligence era and national strategic needs, and to promote the application and development of artificial intelligence technology in the field of scientific research, on August 23, scholars and experts from 30 institutions including Peking University, Beijing Institute of Scientific Intelligence, and iKKEMLab convened at Zhongguan Xin Yuan, Peking University, to initiate the establishment of the "Global Alliance for Scientific Intelligence Development".8/29/2024 AI4EC Lab Delivers "Computational Electrochemistry" Course at the 2024 Xiamen University Electrochemistry Summer SchoolOn July 12-19, 2024, Professor Cheng Jun, Deputy Director of AI4EC Lab, delivered a "Computational Electrochemistry" course to participants in the 2024 Xiamen University Electrochemistry Research Paradigm Summer School.7/31/2024
AI4EC Lab Delivers "Computational Electrochemistry" Course at the 2024 Xiamen University Electrochemistry Summer SchoolOn July 12-19, 2024, Professor Cheng Jun, Deputy Director of AI4EC Lab, delivered a "Computational Electrochemistry" course to participants in the 2024 Xiamen University Electrochemistry Research Paradigm Summer School.7/31/2024 Collaborative Achievement Released at WAIC - "AISI Beyond Boundaries: Exploring Fundamental Research Forum for Next-Generation Large Models"AI4EC Lab, in collaboration with the Beijing Institute of Scientific Intelligence and DeepModeling Technologies, has developed and launched DPA-DynaCat, a universal potential function model for dynamic catalytic elementary reactions on metal nanocluster surfaces, to accelerate the calculation and prediction of dynamic properties of metal nanocatalysts under reaction conditions.7/13/2024
Collaborative Achievement Released at WAIC - "AISI Beyond Boundaries: Exploring Fundamental Research Forum for Next-Generation Large Models"AI4EC Lab, in collaboration with the Beijing Institute of Scientific Intelligence and DeepModeling Technologies, has developed and launched DPA-DynaCat, a universal potential function model for dynamic catalytic elementary reactions on metal nanocluster surfaces, to accelerate the calculation and prediction of dynamic properties of metal nanocatalysts under reaction conditions.7/13/2024 DynaCat@Apps|AI4EC Lab Intelligent Computing Software Package for Dynamic CatalysisAI4EC Lab launched its first automated potential function training and free energy calculation software package for dynamic catalysis research in April 2024 - ai²-cat (https://github.com/AI4EC/ai2-kit). This package comprehensively considers the coupling between the dynamic effects of catalyst structures and reaction processes under real catalytic reaction conditions. By combining active learning strategies with enhanced sampling algorithms, it trains high-precision machine learning potential functions for long-time-scale molecular dynamics simulations of specific catalytic systems and calculates reaction free energies in conjunction with enhanced sampling algorithms. ai²-cat can facilitate efficient catalytic reaction simulations and property calculations, promoting the transition of catalytic research from static to dynamic, and helping to build a new computational catalysis model based on high-throughput automated calculations and AI models.6/13/2024
DynaCat@Apps|AI4EC Lab Intelligent Computing Software Package for Dynamic CatalysisAI4EC Lab launched its first automated potential function training and free energy calculation software package for dynamic catalysis research in April 2024 - ai²-cat (https://github.com/AI4EC/ai2-kit). This package comprehensively considers the coupling between the dynamic effects of catalyst structures and reaction processes under real catalytic reaction conditions. By combining active learning strategies with enhanced sampling algorithms, it trains high-precision machine learning potential functions for long-time-scale molecular dynamics simulations of specific catalytic systems and calculates reaction free energies in conjunction with enhanced sampling algorithms. ai²-cat can facilitate efficient catalytic reaction simulations and property calculations, promoting the transition of catalytic research from static to dynamic, and helping to build a new computational catalysis model based on high-throughput automated calculations and AI models.6/13/2024 Exploring Battery Intelligent Computing, Accelerating Electrolyte Material DesignEnvironmental issues have always been strategic concerns for countries worldwide. The efficient utilization of clean energy (such as hydro, wind, geothermal, and solar energy) has become a key aspect of solving environmental problems and achieving sustainable development. However, the application of clean energy is limited by factors such as geographical location and seasonality. To improve its utilization rate, higher-performance secondary battery energy storage systems must be developed. Among them, lithium-ion batteries, due to their excellent energy storage systems, have been commercialized on a large scale. Secondary battery energy storage systems have received extensive research in recent years. However, as the "blood" of these systems, electrolyte performance determines all battery indicators. Designing electrolyte materials through computational electrochemistry has become a hot research topic in recent years. However, traditional frontier orbital theory calculations cannot accurately describe the complex chemical environment of electrolytes and cannot design electrolyte formulations.5/31/2024
Exploring Battery Intelligent Computing, Accelerating Electrolyte Material DesignEnvironmental issues have always been strategic concerns for countries worldwide. The efficient utilization of clean energy (such as hydro, wind, geothermal, and solar energy) has become a key aspect of solving environmental problems and achieving sustainable development. However, the application of clean energy is limited by factors such as geographical location and seasonality. To improve its utilization rate, higher-performance secondary battery energy storage systems must be developed. Among them, lithium-ion batteries, due to their excellent energy storage systems, have been commercialized on a large scale. Secondary battery energy storage systems have received extensive research in recent years. However, as the "blood" of these systems, electrolyte performance determines all battery indicators. Designing electrolyte materials through computational electrochemistry has become a hot research topic in recent years. However, traditional frontier orbital theory calculations cannot accurately describe the complex chemical environment of electrolytes and cannot design electrolyte formulations.5/31/2024 《Journal of the American Chemical Society》:基于机器学习分子动力学加速水系有机液流电池电解液氧化还原电位和酸度常数计算厦门大学程俊教授团队与嘉庚创新实验室AI4EC Lab通过机器学习加速分子动力学、自动化工作流等方法,基于全原子高精度模拟计算物理化学性质,实现有机电解液设计,为在高溶解度环境(如浓水电解质、水包离子液体和混合电解质等)中高通量计算筛选用于氧化还原流动电池的有机分子创造了新的可能性。相关研究成果以“Accelerating Computation of Acidity Constants and Redox Potentials for Aqueous Organic Redox Flow Batteries by Machine Learning Potential Based Molecular Dynamics”为题发表在JACS期刊5/31/2024
《Journal of the American Chemical Society》:基于机器学习分子动力学加速水系有机液流电池电解液氧化还原电位和酸度常数计算厦门大学程俊教授团队与嘉庚创新实验室AI4EC Lab通过机器学习加速分子动力学、自动化工作流等方法,基于全原子高精度模拟计算物理化学性质,实现有机电解液设计,为在高溶解度环境(如浓水电解质、水包离子液体和混合电解质等)中高通量计算筛选用于氧化还原流动电池的有机分子创造了新的可能性。相关研究成果以“Accelerating Computation of Acidity Constants and Redox Potentials for Aqueous Organic Redox Flow Batteries by Machine Learning Potential Based Molecular Dynamics”为题发表在JACS期刊5/31/2024 AI4EC Lab Intelligent Spectroscopy Exchange WorkshopCurrently, Xiamen City and iKKEMLab are collaborating to build a smart energy storage large infrastructure for future energy chemistry research, aiming to solve numerous scientific and engineering challenges in condition research. This infrastructure will achieve real-time "detection-analysis-control" closed-loop condition characterization of electrochemical devices, where artificial intelligence models play a key role as the central brain for detection, analysis, and control. AI4EC Lab is actively collaborating with experimental teams related to the smart energy storage large infrastructure to realize this closed-loop research prototype for a specific electrochemical device in the short term, actively cooperating in aspects such as data collection and artificial intelligence model construction.5/24/2024
AI4EC Lab Intelligent Spectroscopy Exchange WorkshopCurrently, Xiamen City and iKKEMLab are collaborating to build a smart energy storage large infrastructure for future energy chemistry research, aiming to solve numerous scientific and engineering challenges in condition research. This infrastructure will achieve real-time "detection-analysis-control" closed-loop condition characterization of electrochemical devices, where artificial intelligence models play a key role as the central brain for detection, analysis, and control. AI4EC Lab is actively collaborating with experimental teams related to the smart energy storage large infrastructure to realize this closed-loop research prototype for a specific electrochemical device in the short term, actively cooperating in aspects such as data collection and artificial intelligence model construction.5/24/2024 《Angewandte Chemie International Edition》:机器学习分子动力学模拟揭示表面预熔调控催化活性新机制近日,厦门大学程俊教授课题组和AI4EC Lab,基于机器学习分子动力学模拟与自由能计算方法研究纳米催化剂的表面结构动态效应与反应之间的耦合,取得重要进展。相关研究成果以“Machine Learning Molecular Dynamics Shows Anomalous Entropic Effect on Catalysis via Surface Pre-melting of Nanoclusters”为题发表在Angewandte Chemie International Edition.4/30/2024
《Angewandte Chemie International Edition》:机器学习分子动力学模拟揭示表面预熔调控催化活性新机制近日,厦门大学程俊教授课题组和AI4EC Lab,基于机器学习分子动力学模拟与自由能计算方法研究纳米催化剂的表面结构动态效应与反应之间的耦合,取得重要进展。相关研究成果以“Machine Learning Molecular Dynamics Shows Anomalous Entropic Effect on Catalysis via Surface Pre-melting of Nanoclusters”为题发表在Angewandte Chemie International Edition.4/30/2024 《Angewandte Chemie International Edition》:理论光谱计算和实验测量合力揭示石墨烯-水界面的微观结构近日,厦门大学萨本栋微米纳米研究院/嘉庚创新实验室AI4EC Lab的汤富杰课题组与德国马普学会高分子研究所的Yuki Nagata和Mischa Bonn课题组合作,通过结合理论光谱计算和实验测量,研究了石墨烯-水界面的微观结构,取得了重要进展。相关成果已以“Heterodyne-Detected Sum-Frequency Generation Vibrational Spectroscopy Reveals Aqueous Molecular Structure at the Suspended Graphene/Water Interface”为题发表在Angewandte Chemie International Edition3/31/2024
《Angewandte Chemie International Edition》:理论光谱计算和实验测量合力揭示石墨烯-水界面的微观结构近日,厦门大学萨本栋微米纳米研究院/嘉庚创新实验室AI4EC Lab的汤富杰课题组与德国马普学会高分子研究所的Yuki Nagata和Mischa Bonn课题组合作,通过结合理论光谱计算和实验测量,研究了石墨烯-水界面的微观结构,取得了重要进展。相关成果已以“Heterodyne-Detected Sum-Frequency Generation Vibrational Spectroscopy Reveals Aqueous Molecular Structure at the Suspended Graphene/Water Interface”为题发表在Angewandte Chemie International Edition3/31/2024 《SCIENTIA SINICA Chimica》:探讨面向能源电化学的新一代表征方法 ——从工况表征到人工智能厦门大学田中群院士及其同事们在讨论谱学电化学发展脉络和分析非原位、原位和工况三类表征的本质性区别的基础上,展望面向新型电化学能源器件/系统的新一代工况表征实验和理论方法。1/31/2024
《SCIENTIA SINICA Chimica》:探讨面向能源电化学的新一代表征方法 ——从工况表征到人工智能厦门大学田中群院士及其同事们在讨论谱学电化学发展脉络和分析非原位、原位和工况三类表征的本质性区别的基础上,展望面向新型电化学能源器件/系统的新一代工况表征实验和理论方法。1/31/2024