Background
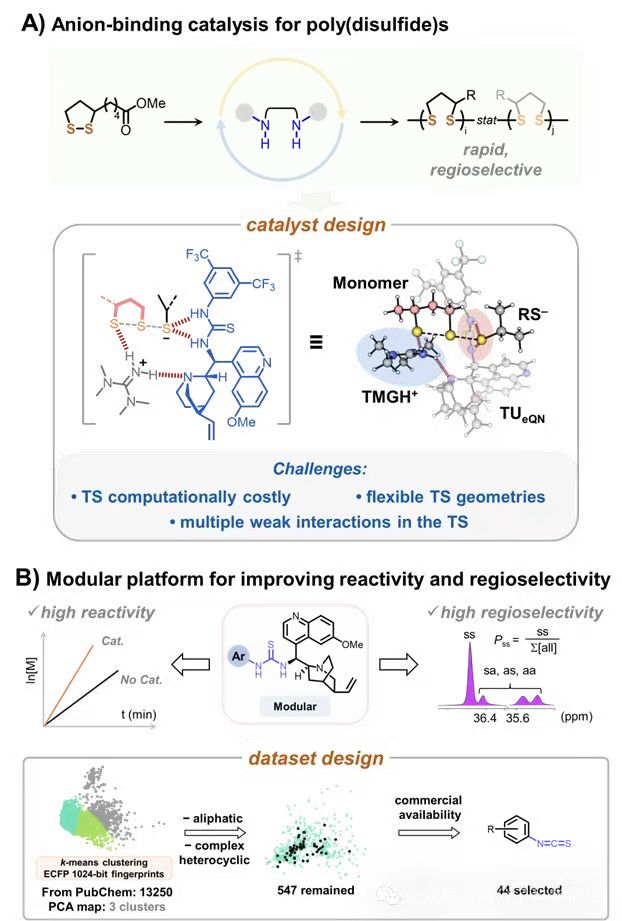
By integrating machine learning with mechanistic chemistry, the team established a data-driven workflow for catalyst discovery and interpretation. From 13,250 isothiocyanates in PubChem, principal component analysis (PCA) and k-means clustering guided the selection of 44 epiquinine-derived thiourea catalysts bearing ortho/meta/para aryl substituents (Figure 1).
NMR spectroscopy, a non-destructive, site-sensitive probe of local environments, was used to quantify polymerization kinetics and regioregularity in solution. While NMR captures averaged signals over local structures and dynamics—often obscuring direct structure–spectrum relationships—the team combined targeted quantum chemistry and data-driven descriptor engineering to rationalize observed shifts and trends beyond traditional static DFT analyses.
Experimental overview
Experimental overview Using (R)-methyl lipoate as the model monomer, the team quantified:
· Reactivity: apparent first-order propagation rate constant (kp) via 1H NMR
· Regioselectivity: population of regioregular triads (Pss) via 13C NMR
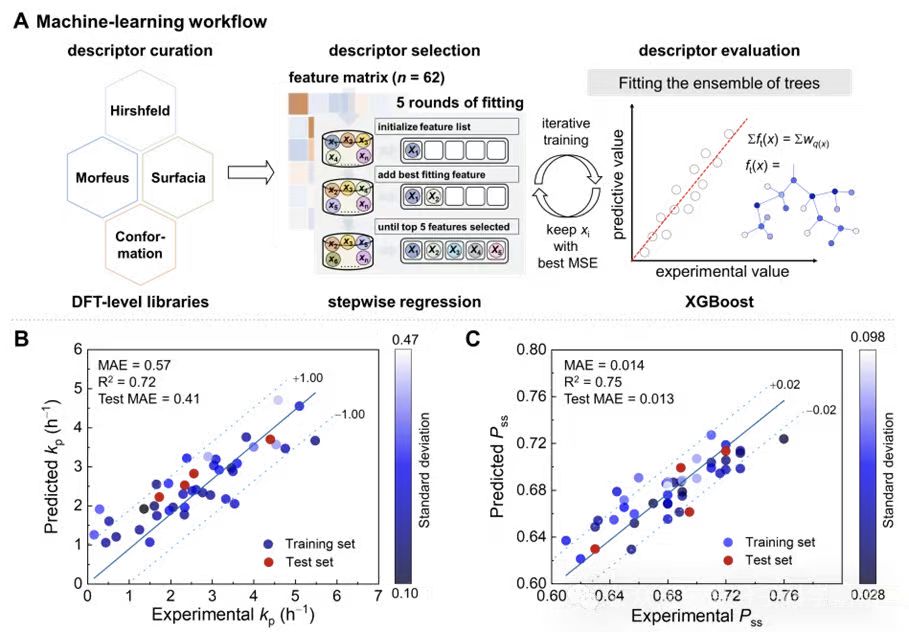
Across the 44 catalysts, reactivity spanned nearly two orders of magnitude (0.15–7.31 h−1), while Pss varied within 0.61–0.76. An XGBoost model with stepwise feature selection was trained on 62 chemically informed descriptors, and SHAP analysis was used to interpret feature contributions (Figures 2–4).
Key findings
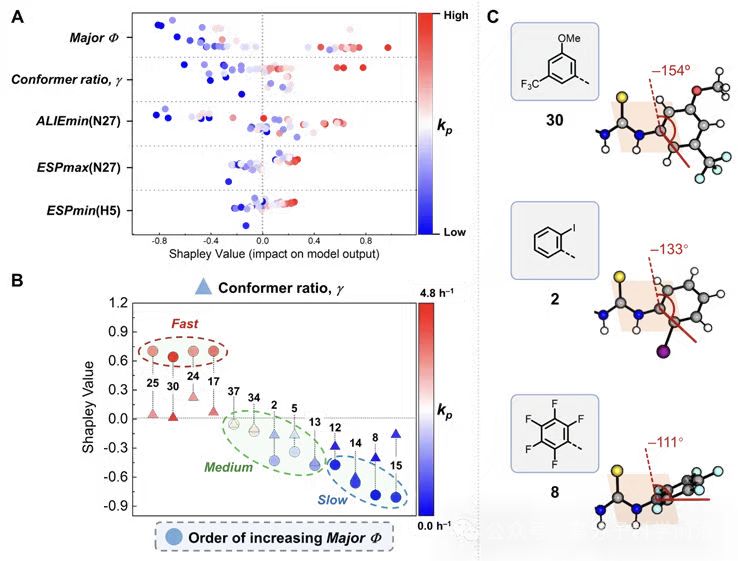
· Reactivity drivers: Conformational features dominate.
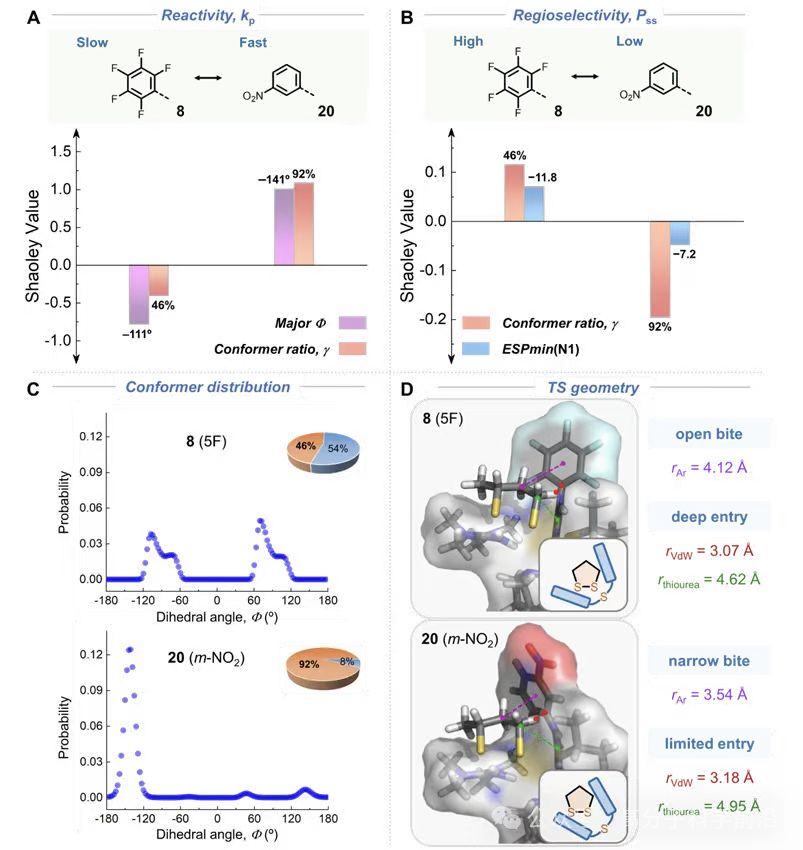
Major dihedral (Major Φ) of the aryl ring relative to the thiourea plane and conformer ratio (γ) are decisive. More coplanar aryl rings and fewer rotamers increase kp. For example, meta-NO2 (catalyst 20) shows high reactivity linked to conformational preorganization (Figure 3).
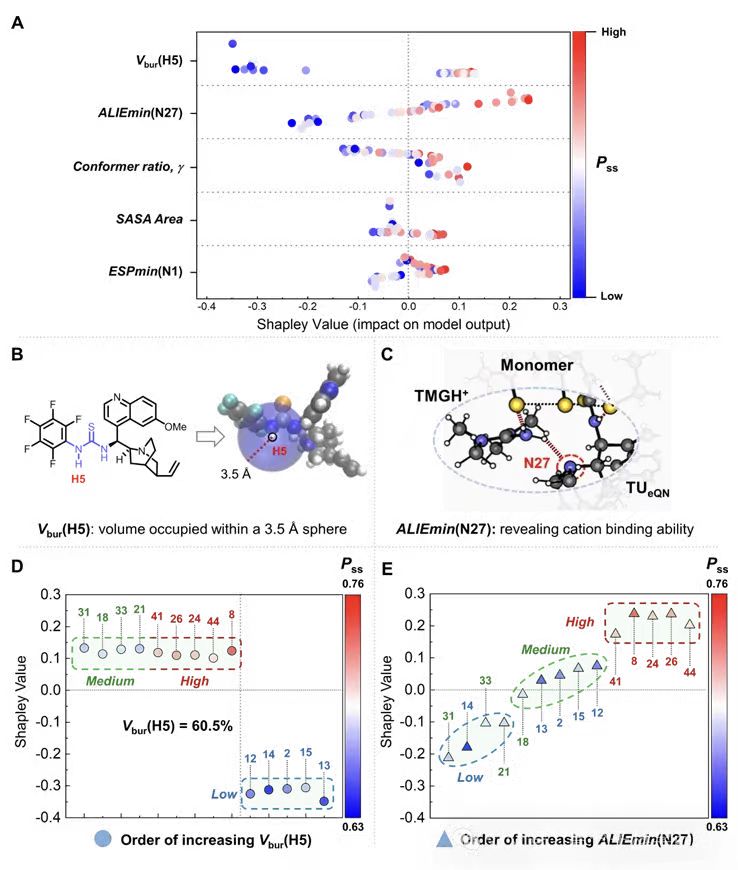
· Regioselectivity drivers: Synergy of steric and electronic factors.
o Sterics at the aryl-side NH site, Vbur(H5), exhibits an upper threshold—excessive buried volume lowers Pss.
Electron donation ability at the tertiary amine, ALIEmin(N27), and the polarity at the aryl-side NH (ESP/ALIE metrics) modulate Pss. Electron-withdrawing groups enhance favorable π–vdW contacts with the monomer and promote selectivity (Figure 4).
· Reactivity–selectivity trade-off:
o Electron-donating substituents tend to enhance cation stabilization and reactivity but weaken the aryl–monomer vdW interaction that favors selective insertion; electron-withdrawing groups do the opposite.
o Halogen/(pseudo)halogen substituents (e.g., 24, 25, 26, 40) deliver a balanced optimum—adequate electrophilicity with minimal steric penalty—outperforming previous designs.
Mechanistic validation
· DFT supports the data-driven insights:
o The most selective catalyst (8) forms a tighter transition state with shorter aryl–monomer vdW contact (by ~0.11 Å), consistent with higher Pss.
The most reactive catalyst (20) benefits from a dominant binding conformer, enabling efficient preorganization and accelerated propagation (Figure 5).
· Agreement between SHAP-derived feature attributions and DFT rationalizations substantiates the proposed TS stabilization picture: thiourea anion-binding, tertiary amine–countercation organization, and aryl-surface vdW engagement jointly govern outcomes.
Significance and outlook
This work demonstrates a systematic data-science framework for deciphering transition-state stabilization in polymerization catalysis, establishing practical design rules:
· Conformational preorganization boosts reactivity.
· Moderate sterics at the aryl NH and electron-withdrawing character favor regioselectivity.
· Halogenation emerges as a robust strategy to balance the reactivity–selectivity trade-off.
The approach paves the way for rational, data-guided design across broader organocatalyst backbones and polymerization types.
Authors
· Yuming Su: Co-first author. Assistant Research Fellow (since 2024), Laboratory of AI for Electrochemistry (AI4EC), Tan Kah Kee Innovation Laboratory, Xiamen University (Prof. Cheng Wang’s group). Research focuses on interpretable ML for structure–activity relationships and intelligent decision-making for operando characterization. First/co-first author of 6 papers in journals including JACS, Angewandte, and Advanced Science; >400 citations; H-index 11.
· Yun Liu: Principal Investigator, College of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Peking University; Recipient of NSFC Excellent Young Scientists Fund (Overseas, 2022). Ph.D. in Chemistry, Indiana University (2017); postdoc at UIUC Beckman Institute with Prof. Jeffrey S. Moore (2017–2021); Independent PI at PKU since 2021. Research areas: dynamic polymer synthesis and polymer physical chemistry.
· Cheng Wang: Professor, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University; National-level Young Talent; 2020 Youth Chemist Award (Chinese Chemical Society). B.S. Peking University (2009); Ph.D. UNC Chapel Hill (2013, MOF catalysis); Postdoc, University of Chicago (2013–2015, femtosecond spectroscopy). >120 publications, >10,000 citations. Current interests: MOL design and catalytic applications; 3D-printed photonic porous materials; AI-guided catalyst development (including CO2 electroreduction, hydrogen isotope separation, peptide-aided photocatalysis), pioneering ML and LLMs for catalyst design and mechanistic analysis.
DOI:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.202502090
