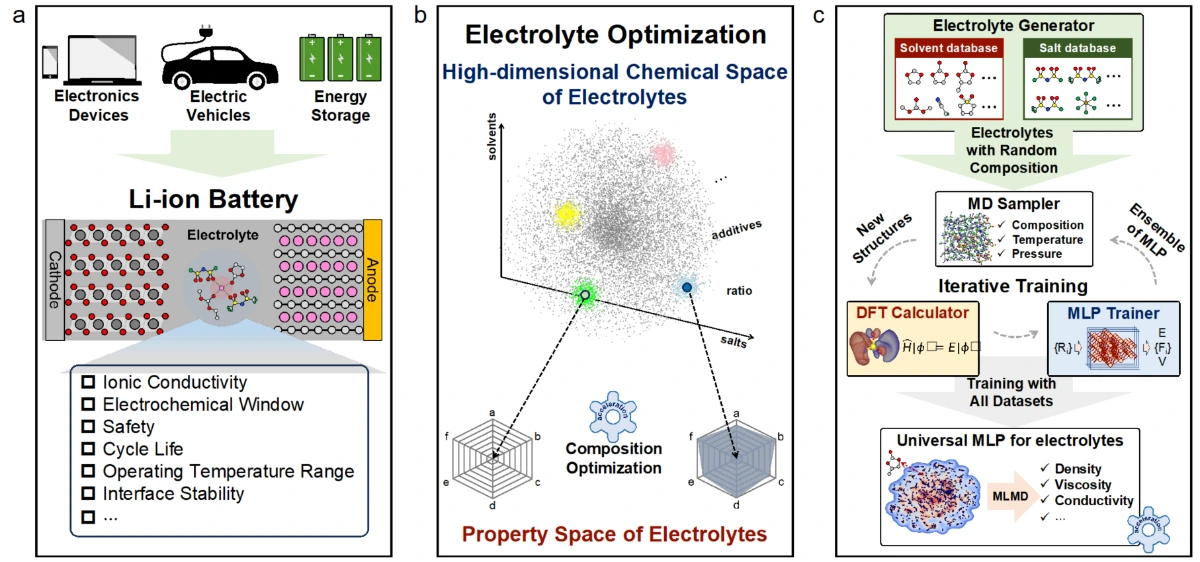
Domain Oriented Universal Machine Learning Potential Enables Fast Exploration of Chemical Space of Battery Electrolytes
Li-ion batteries, widely used in electronic devices, electric vehicles, and aviation, demand high energy density, fast charging capabilities, and broad operating temperature ranges. Computations combined with experiments have gained increasing attention for electrolyte development. However, the inherent complexity of electrolytes poses a significant challenge. Classical molecular dynamics often fails due to inaccuracies in force field parameters, while ab initio calculations are limited by high computational costs. Recently, machine learning molecular dynamics has emerged as an efficient and accurate alternative. However, its application is hindered by limited transferability of machine learning potentials. In this work, we developed a universal machine learning potential for electrolytes using an iterative training approach on randomly composed datasets, enabling the accurate computation of key properties for a broad range of electrolytes via molecular dynamics. Furthermore, coordination dynamics analysis of Li ion, by quantifying the coordination lifetime, provides a direct, quantitative measure of solvation strength. The universal machine learning potential for electrolytes facilitates the prediction and optimization of electrolyte properties, offering a powerful tool for electrolyte design.