Revealing Transition State Stabilization in Organocatalytic Ring-Opening Polymerization Using Data Science
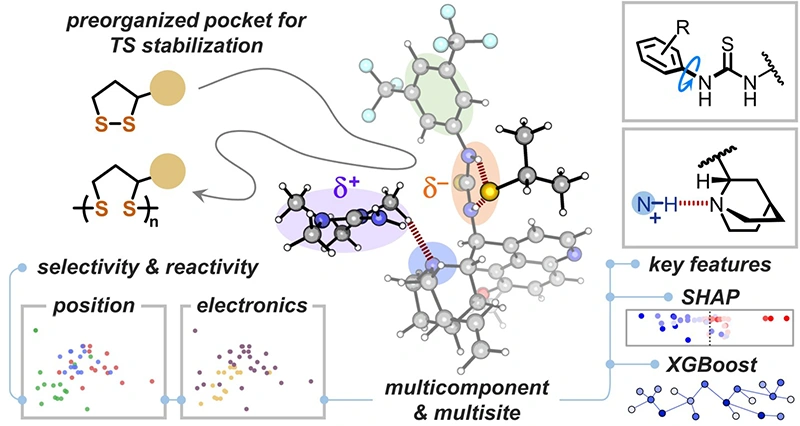
In nature, enzymes leverage constituent amino acid residues to create catalytically active sites to effect high reactivity and selectivity. Multicomponent host–guest assemblies have been exploited to mimic enzymatic microenvironments by pre-organizing a network of noncovalent interactions. While organocatalysts such as thioureas have gained widespread success in organic transformation and controlled polymerization, evaluation of the participating structural features in the transition state (TS) remains challenging. Herein, we report the use of data science tools, i.e., a decision-tree-based machine-learning algorithm and Shapley additive explanations (SHAP) analysis, to model reactivity and regioselectivity in a thiourea-catalyzed ring-opening polymerization of 1,2-dithiolanes. Variation of aryl substituent position and electronic characteristics reveals key catalyst features involved in the TS. The analysis of feature importance helps explain the reason behind the optimal performance of (pseudo) halogen-substituted catalysts. Furthermore, the structural basis for the unveiled reactivity-regioselectivity trade-off in the catalysis are established.